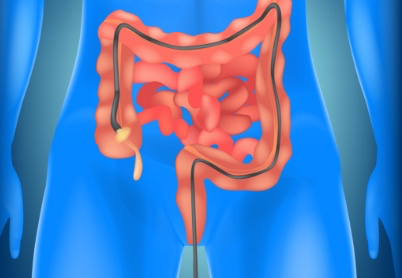
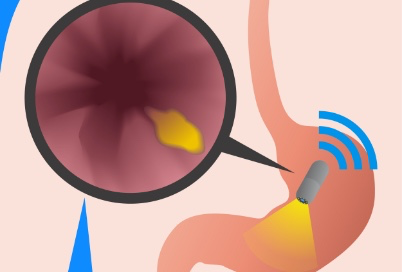
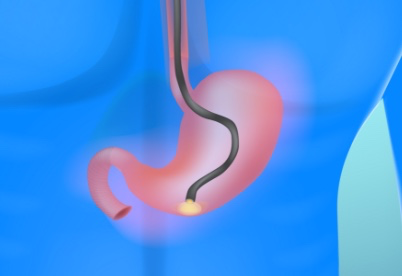
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding refers to any bleeding that occurs anywhere in the digestive tract – as from the esophagus to the colon. It can be the result of ulcers, inflammation, polyps, hemorrhoids, GI cancers, or other digestive disorders. GI bleeding may be obvious (such as bright red blood in the stool) or hidden and detected through tests. Early evaluation and diagnosis are key to effective treatment and preventing complications like anemia.
Treatments & Procedures
Blood
Tests
Imaging
Tests

Physical
Examination
Stool Tests
- Common Symptoms
GI bleeding can present in various ways, including:
- Bright red blood in stool
- Black, tarry stools
- Blood in vomit or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
- Pale skin
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Pale skin
- Unexplained abdominal pain
- Frequently Asked Questions
Causes may include ulcers, hemorrhoids, inflammation, polyps, or cancers of the digestive tract.
No, some bleeding may be hidden and only detected through lab tests or stool studies.
Gastrointestinal bleeding should be evaluated promptly, especially if it is heavy, ongoing, or associated with weakness or dizziness.