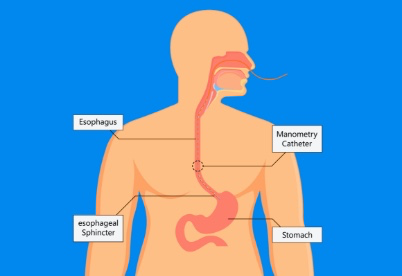
The esophagus is a long, muscular tube that connects your throat to your stomach. Esophageal manometry is a test that shows whether your esophagus is working properly.
No Referral Required
When you swallow, your esophagus contracts and pushes food into your stomach. Esophageal manometry measures the contractions.
The test also measures the force and coordination of esophageal muscles as they move food to your stomach.
During esophageal manometry, a thin, flexible tube (catheter) that contains pressure sensors is passed through your nose, down your esophagus and into your stomach. Esophageal manometry can be helpful in diagnosing certain disorders that can affect your esophagus.
Why It's Done
Your doctor might recommend esophageal manometry if you’re having symptoms that could be related to an esophageal disorder.
Esophageal manometry provides information about the movement of food through the esophagus into the stomach. The test measures how well the muscles at the top and bottom of your esophagus (sphincter muscles) open and close, as well as the pressure, speed and pattern of the wave of esophageal muscle contractions that moves food along.
If your main symptom is difficulty swallowing or pain when swallowing, your doctor is likely to order other tests, such as X-rays or upper endoscopy — a procedure by which your doctor can see your upper digestive system with a tiny camera on the end of a tube — before or instead of esophageal manometry. These tests identify or rule out a narrowing, a complete blockage or an area of inflammation in your esophagus.
Esophageal manometry might be used to help diagnose:
- Diffuse esophageal spasm. This rare swallowing problem is characterized by multiple, forceful, poorly coordinated muscle contractions of your esophagus.
- Achalasia. This uncommon condition occurs when your lower esophageal sphincter muscle doesn’t relax properly to let food enter your stomach. This can cause difficulty swallowing and regurgitation of food back up into your throat.
- Scleroderma. In many people with this rare progressive disease, the muscles in the lower esophagus stop moving, leading to severe gastroesophageal reflux.
What You Can Expect
Esophageal manometry can be performed using conventional manometry or high-resolution manometry. High-resolution manometry uses more pressure sensors and is more accurate at assessing pressure changes than is conventional manometry.
This test is done as an outpatient procedure without sedation.
During esophageal manometry
- While you are sitting up, a member of your health care team sprays your throat with a numbing medication or puts numbing gel in your nose or both.
- A catheter is guided through your nose into your esophagus. The catheter may be covered by a water-filled sleeve. It doesn’t interfere with your breathing. However, your eyes might water, and you might gag. You might have a slight nosebleed from irritation.
- After the catheter is in place, you’ll be asked to lie on your back on an exam table or to remain seated.
- You then swallow small sips of water. As you do, a computer connected to the catheter records the pressure, speed and pattern of your esophageal muscle contractions.
- During the test, you’ll be asked to breathe slowly and smoothly, remain as still as possible, and swallow only when you’re asked to do so.
- A member of your health care team might move the catheter up or down into your stomach while the catheter continues its measurements.
- The catheter then is slowly withdrawn.
The test usually lasts about 30 minutes.
After esophageal manometry
When your esophageal manometry is complete, you can return to your normal activities.
